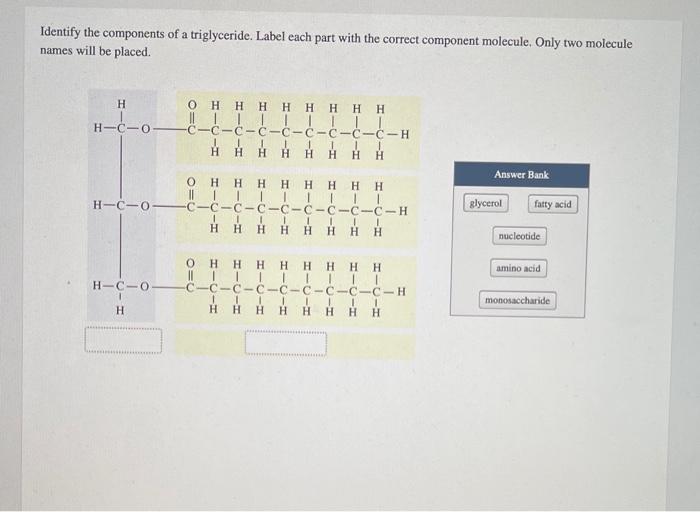
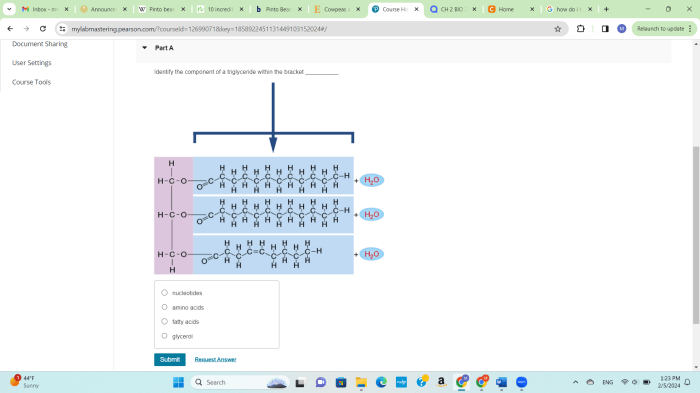
Identify the component of a triglyceride within the bracket – In the realm of biochemistry, the identification of the three fatty acids present in a triglyceride is a fundamental endeavor, providing insights into the structure and properties of these essential molecules. Triglycerides, composed of a glycerol backbone esterified to three fatty acids, play a pivotal role in lipid metabolism and energy storage.
Understanding their composition is crucial for comprehending their physiological functions and implications in health and disease.
This comprehensive exploration delves into the structure and bonding of these fatty acids, elucidating the distinct characteristics of saturated, unsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids. The process of triglyceride synthesis in the body is meticulously described, highlighting the intricate interplay of enzymes and coenzymes.
Furthermore, the catabolism and anabolism of triglycerides are examined, shedding light on the intricate regulation of triglyceride metabolism by hormones.
Components of a Triglyceride: Identify The Component Of A Triglyceride Within The Bracket
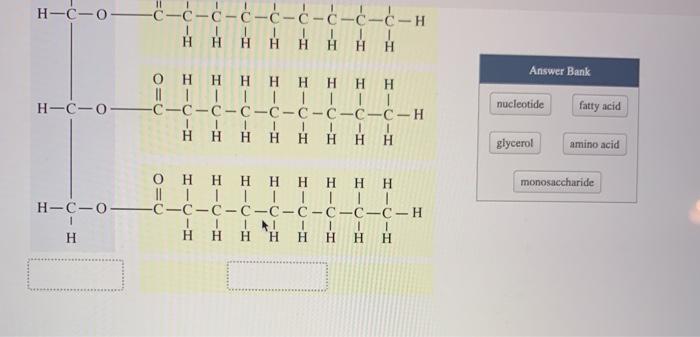
Triglycerides are composed of a glycerol molecule bonded to three fatty acids. These fatty acids can be identical or different, resulting in a variety of triglyceride structures.
The fatty acids in a triglyceride are long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxyl group (-COOH) at one end. The length of the chain and the number of double bonds determine the properties of the fatty acid.
Fatty Acid Composition
Fatty acids are classified into three types based on the number of double bonds in their carbon chain:
- Saturated fatty acidshave no double bonds and are typically solid at room temperature.
- Unsaturated fatty acidshave one or more double bonds and are typically liquid at room temperature.
- Polyunsaturated fatty acidshave multiple double bonds and are typically liquid at room temperature.
Examples of saturated fatty acids include palmitic acid and stearic acid. Examples of unsaturated fatty acids include oleic acid and linoleic acid. Examples of polyunsaturated fatty acids include linolenic acid and arachidonic acid.
Triglyceride Synthesis
Triglycerides are synthesized in the body through a series of enzymatic reactions. The first step is the activation of fatty acids by the enzyme acyl-CoA synthetase. The activated fatty acids are then transferred to glycerol-3-phosphate by the enzyme glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase.
The resulting molecule is diacylglycerol-3-phosphate, which is then converted to triglyceride by the enzyme phosphatidate phosphohydrolase.
The synthesis of triglycerides is regulated by a number of hormones, including insulin, glucagon, and epinephrine.
Triglyceride Metabolism
Triglycerides are catabolized through a process called lipolysis. Lipolysis is the breakdown of triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol. Fatty acids are then oxidized to produce energy, while glycerol is converted to glucose.
The catabolism of triglycerides is regulated by a number of hormones, including insulin, glucagon, and epinephrine.
Triglycerides in Health and Disease, Identify the component of a triglyceride within the bracket
Triglycerides are an important source of energy for the body. However, high levels of triglycerides in the blood can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
High levels of triglycerides are associated with obesity and diabetes. Triglycerides are also a risk factor for pancreatitis.
FAQ Compilation
What are the three fatty acids present in a triglyceride?
Triglycerides consist of a glycerol backbone esterified to three fatty acids, which can vary in their chain length, degree of saturation, and presence of functional groups.
How are fatty acids bonded to the glycerol backbone?
Fatty acids are attached to the glycerol backbone through ester linkages, forming covalent bonds between the carboxyl group of the fatty acid and the hydroxyl group of the glycerol.
What is the difference between saturated, unsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids?
Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds between their carbon atoms, while unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds. Polyunsaturated fatty acids contain multiple double bonds, often separated by methylene groups.