Embark on an educational journey with our comprehensive elements compounds & mixtures worksheet answer key. This invaluable resource delves into the fundamental concepts of chemistry, providing a clear understanding of the structure and properties of matter. From the basic building blocks of elements to the complex interactions within compounds and mixtures, this answer key unravels the intricate tapestry of the chemical world.
Delving into the depths of chemistry, we explore the unique characteristics of elements, the formation and properties of compounds, and the diverse nature of mixtures. With each concept meticulously explained and supported by real-world examples, this answer key transforms the study of chemistry into an engaging and enlightening experience.
Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
In chemistry, matter can be classified into three main categories: elements, compounds, and mixtures. Each of these categories has distinct properties and characteristics.
Elements
Elements are the fundamental building blocks of matter. They cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
- Examples of elements include hydrogen, oxygen, gold, and carbon.
- Elements have unique atomic numbers, which determine their chemical properties.
- Elements can exist as solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature.
Compounds
Compounds are substances that are composed of two or more elements chemically bonded together.
- Examples of compounds include water (H 2O), salt (NaCl), and sugar (C 12H 22O 11).
- Compounds have specific molecular structures and properties that are different from the elements that compose them.
- Compounds can be formed when elements react with each other in chemical reactions.
Mixtures, Elements compounds & mixtures worksheet answer key
Mixtures are combinations of two or more elements or compounds that are not chemically bonded together.
- Examples of mixtures include air, seawater, and concrete.
- Mixtures can be homogeneous (uniform in composition) or heterogeneous (non-uniform in composition).
- Mixtures can be separated into their components by physical means, such as filtration or distillation.
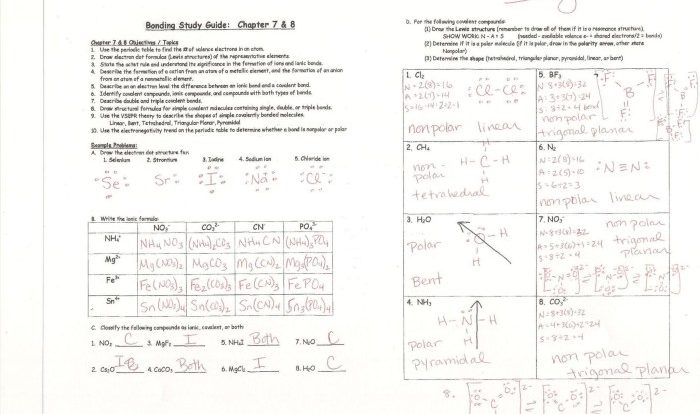
Worksheet Answer Key
| Question | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Define elements. | Elements are the fundamental building blocks of matter that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. | |
| Provide examples of elements. | Hydrogen, oxygen, gold, carbon | |
| Explain the properties of elements. | Elements have unique atomic numbers, can exist in different states at room temperature, and have distinct chemical properties. | |
| Define compounds. | Compounds are substances composed of two or more elements chemically bonded together. | |
| Provide examples of compounds. | Water (H2O), salt (NaCl), sugar (C12H22O11) | |
| Explain the properties of compounds. | Compounds have specific molecular structures and properties that differ from the elements that compose them. | |
| Discuss how compounds are formed. | Compounds are formed when elements react with each other in chemical reactions. | |
| Define mixtures. | Mixtures are combinations of two or more elements or compounds that are not chemically bonded together. | |
| Provide examples of mixtures. | Air, seawater, concrete | |
| Explain the properties of mixtures. | Mixtures can be homogeneous or heterogeneous, and can be separated into their components by physical means. | |
| Discuss how mixtures are formed. | Mixtures are formed when different substances are physically combined without undergoing chemical reactions. |
Key Questions Answered: Elements Compounds & Mixtures Worksheet Answer Key
What is the difference between an element and a compound?
An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. A compound, on the other hand, is a substance composed of two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions.
How are mixtures formed?
Mixtures are formed when two or more substances are physically combined without any chemical bonding. The components of a mixture retain their individual properties and can be separated by physical means, such as filtration or distillation.