Welcome to the captivating world of the Mouths of the Ganges Map! This geographical masterpiece showcases the grandeur of the Ganges River as it gracefully meanders through the fertile plains of India and Bangladesh, shaping the landscape and enriching the lives of millions.
From its humble origins in the Himalayas to its majestic confluence with the Bay of Bengal, the Ganges River has played a pivotal role in the history, culture, and economy of the region. Dive into this comprehensive guide to discover the intricate details of the Ganges River delta, its physical characteristics, ecological diversity, and socioeconomic importance.
Overview of the Mouths of the Ganges: Mouths Of The Ganges Map
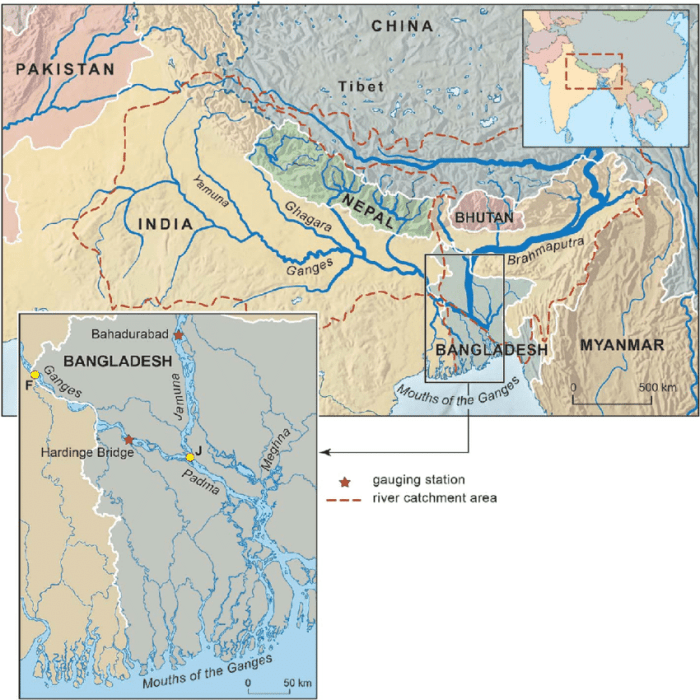
The Ganges River delta is a vast, fertile region located in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent. It is formed by the confluence of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers and covers an area of approximately 105,000 square kilometers.
The delta is located in the states of West Bengal in India and Bangladesh and is one of the most densely populated regions in the world.
Studying the mouths of the Ganges map can be a great way to visualize the vastness of this river system. If you’re looking for more educational resources, check out the math 2 released test nc for practice materials. Returning to our topic, the mouths of the Ganges map provide a detailed overview of the river’s distributaries and their impact on the surrounding landscape.
The Ganges River is considered sacred by Hindus and is a major pilgrimage destination. The delta is also home to a number of important historical and cultural sites, including the ancient city of Varanasi and the Sunderbans mangrove forest.
Geographical Location, Mouths of the ganges map
The Ganges River delta is located in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent. It is bounded by the Bay of Bengal to the south, the Himalayas to the north, and the Aravalli Range to the west. The delta is divided into two parts by the Padma River, which flows through Bangladesh.
The western part of the delta is known as the Sundarbans, while the eastern part is known as the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta.
Significance of the Ganges River
The Ganges River is one of the most important rivers in India and Bangladesh. It provides water for drinking, irrigation, and transportation. The river is also a major source of fish and other aquatic resources. The Ganges River delta is a major agricultural region, and it is home to a large number of people who depend on the river for their livelihoods.
Historical and Cultural Importance
The Ganges River delta has been a major center of human civilization for centuries. The ancient city of Varanasi is located on the banks of the Ganges River, and it is one of the holiest cities in Hinduism. The delta is also home to a number of other important historical and cultural sites, including the Sunderbans mangrove forest and the ruins of the ancient city of Vikrampur.
Physical Geography of the Mouths of the Ganges
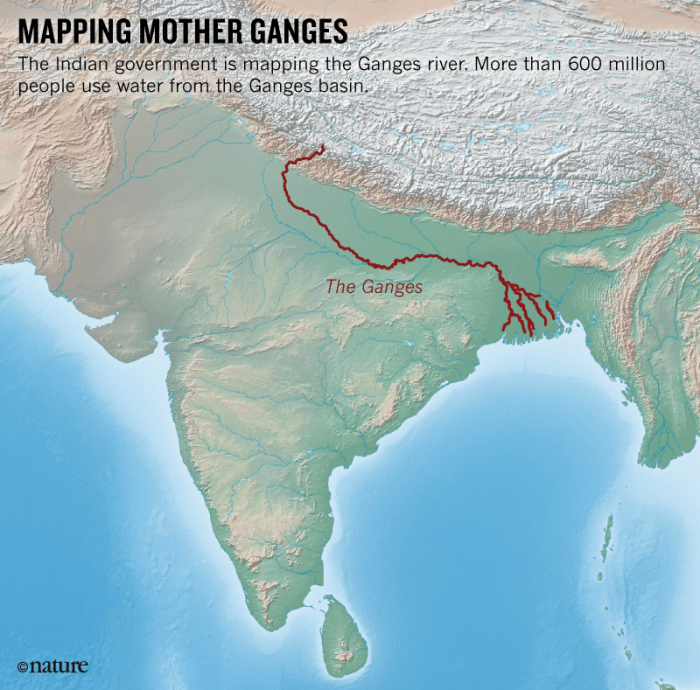
The Ganges River delta is a vast, low-lying region formed by the deposition of sediment at the mouth of the Ganges River. It is one of the largest deltas in the world, covering an area of over 105,000 square kilometers.
The delta is shaped like a triangle, with its apex at the city of Kolkata and its base along the Bay of Bengal. The Ganges River enters the delta at its apex and splits into a number of distributaries, which flow across the delta and empty into the Bay of Bengal.
The delta is a dynamic landscape, constantly changing shape as the Ganges River deposits sediment and erodes its banks. The delta is also subject to flooding, which can cause widespread damage to crops and infrastructure.
Formation and Evolution of the Ganges River Delta
The Ganges River delta began to form about 6,000 years ago, when the Ganges River changed course and began to flow into the Bay of Bengal. Over time, the Ganges River deposited sediment at its mouth, forming a delta. The delta has continued to grow over time as the Ganges River has continued to deposit sediment.
Role of the Ganges River in Shaping the Landscape of the Delta Region
The Ganges River has played a major role in shaping the landscape of the delta region. The river has deposited sediment, which has formed the delta’s landforms. The river has also created a number of oxbow lakes, which are formed when a river changes course and leaves behind a horseshoe-shaped lake.
Hydrology of the Mouths of the Ganges

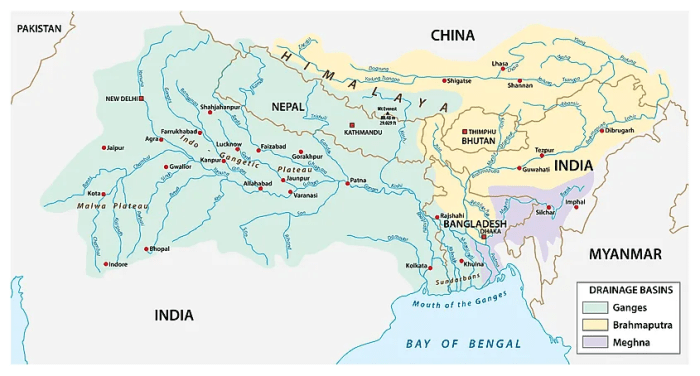
The Ganges River delta, formed by the confluence of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers, is one of the largest and most dynamic river deltas in the world. The hydrology of this region is characterized by complex water flow patterns, sediment transport, and salinity levels, influenced by both natural and human factors.The
Ganges River discharges an enormous volume of water into the Bay of Bengal, estimated at around 1,000 cubic kilometers per year. This freshwater influx significantly alters the salinity levels of the bay, creating a gradient from near-freshwater conditions in the deltaic region to more saline waters offshore.
The river’s flow patterns are influenced by the monsoon seasons, with high discharge during the rainy season and lower discharge during the dry season.The Ganges River delta is a major source of sediment, contributing to the formation of vast mudflats and islands in the Bay of Bengal.
Sediment transport is driven by the river’s flow and tidal currents, and the deposited sediment helps to shape the coastline and provide habitats for diverse marine life.
Challenges and Opportunities of Water Management
Managing water resources in the Ganges River delta presents significant challenges and opportunities. The region is home to a large population that relies on the river for drinking water, irrigation, and transportation. However, increasing water demand, pollution, and climate change pose threats to the sustainability of water resources.Water
management efforts in the delta aim to balance the needs of human populations with the preservation of the ecosystem. This includes implementing measures to reduce pollution, improve water quality, and promote sustainable water use practices. Additionally, the construction of dams and embankments has been undertaken to control flooding and regulate water flow, but these structures can also have environmental impacts.Understanding
the hydrology of the Ganges River delta is crucial for developing effective water management strategies that ensure the long-term sustainability of this vital ecosystem and the well-being of the communities that depend on it.
Ecology of the Mouths of the Ganges
The Ganges River delta is a vast and dynamic ecosystem that supports a wide range of biodiversity. The delta’s diverse habitats, including mangrove forests, wetlands, and marine environments, provide essential breeding and feeding grounds for numerous species.
Mangrove Forests
The mangrove forests of the Ganges delta are among the largest and most diverse in the world. These forests are home to a variety of plant and animal species, including tigers, leopards, crocodiles, and dolphins. The mangroves play a crucial role in protecting the coastline from erosion and storm surges, and they also provide a vital source of food and shelter for fish and other aquatic organisms.
Wetlands
The wetlands of the Ganges delta are a mosaic of freshwater and saltwater habitats that support a rich diversity of plants and animals. These wetlands provide essential breeding and feeding grounds for migratory birds, and they also play an important role in flood control and water purification.
Marine Habitats
The marine habitats of the Ganges delta are home to a variety of fish, shellfish, and other marine organisms. These habitats are important for commercial fishing and they also support a thriving tourism industry.
Biodiversity Hotspot
The Ganges River delta is recognized as one of the world’s biodiversity hotspots. This means that it is home to a large number of endemic species, which are found nowhere else on Earth. The delta’s unique combination of habitats and species makes it a global conservation priority.
Threats to the Ecology of the Ganges River Delta
The ecology of the Ganges River delta is under threat from a variety of human activities, including pollution, deforestation, and overfishing. These activities are degrading the delta’s habitats and reducing its biodiversity.
Conservation Efforts
There are a number of conservation efforts underway to protect the ecology of the Ganges River delta. These efforts include the establishment of protected areas, the restoration of degraded habitats, and the promotion of sustainable fishing practices.
Socioeconomic Importance of the Mouths of the Ganges
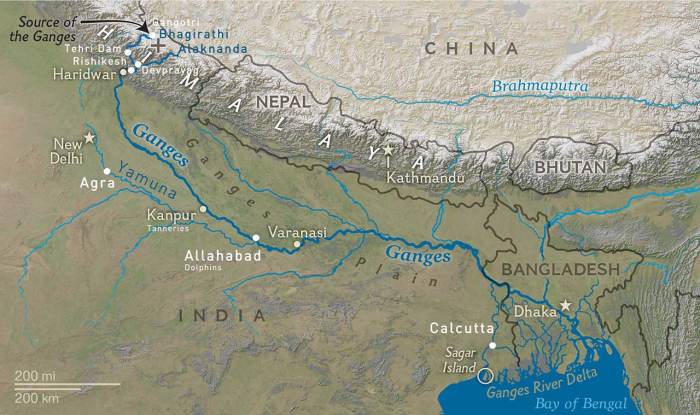
The Ganges River delta, located at the mouths of the Ganges River, is a region of great socioeconomic importance for India and Bangladesh. The delta is home to a large and diverse population, and its fertile soils and abundant water resources support a wide range of economic activities.
Agriculture
The Ganges River delta is one of the most productive agricultural regions in the world. The fertile soils and abundant water supply make it ideal for growing a variety of crops, including rice, jute, and sugarcane. The delta is also home to a large number of livestock, including cattle, buffalo, and goats.
Fisheries
The Ganges River delta is also a major fishing ground. The river and its tributaries are home to a wide variety of fish species, including hilsa, carp, and catfish. Fishing is an important source of food and income for many people in the delta.
Tourism
The Ganges River delta is also a popular tourist destination. The delta is home to a number of historical and religious sites, including the Sundarbans mangrove forest, the world’s largest mangrove forest. The delta is also a popular spot for birdwatching and other wildlife viewing.
Detailed FAQs
What is the significance of the Ganges River delta?
The Ganges River delta is one of the most fertile and densely populated regions in the world, supporting over 400 million people. It is a major source of agricultural productivity, fisheries, and tourism, contributing significantly to the economies of India and Bangladesh.
What are the major physical characteristics of the Ganges River delta?
The Ganges River delta is a vast, low-lying region covering an area of over 100,000 square kilometers. It is characterized by a network of interconnected waterways, including rivers, canals, and distributaries, that form a complex and dynamic ecosystem.
What are the major ecological threats facing the Ganges River delta?
The Ganges River delta is facing a number of ecological threats, including pollution, overfishing, and habitat loss. These threats are putting the biodiversity of the delta at risk and undermining the livelihoods of the people who depend on it.