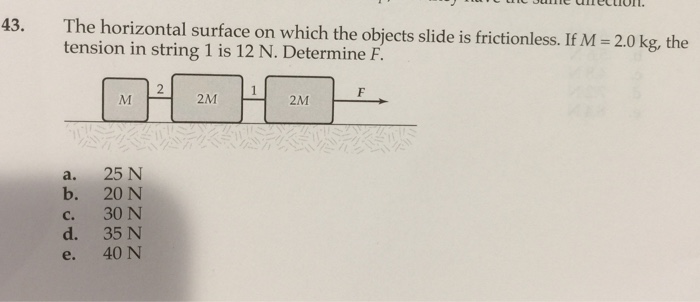
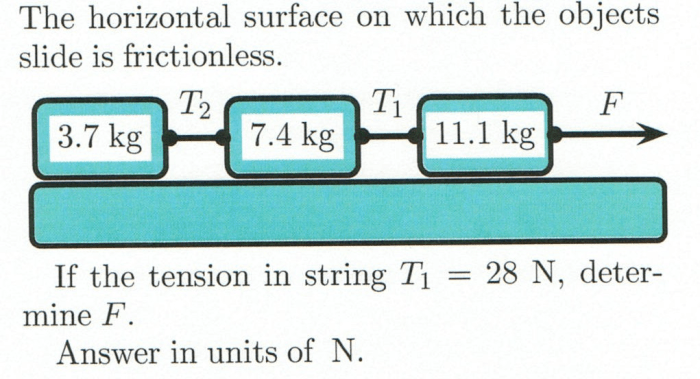
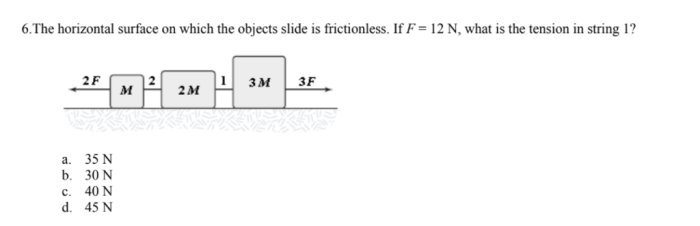
The horizontal surface on which the objects slide is frictionless. – The horizontal surface on which objects slide is frictionless. This unique characteristic has profound implications for the motion of objects, opening up a realm of possibilities in various scientific and engineering applications. Frictionless surfaces eliminate the resistance that typically impedes movement, allowing objects to glide effortlessly with minimal energy loss.
In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the properties of frictionless horizontal surfaces, examining their impact on object interactions and showcasing their practical applications. We will also design an experiment to demonstrate these properties and discuss potential future advancements in frictionless surface technologies.
Horizontal Surface Properties: The Horizontal Surface On Which The Objects Slide Is Frictionless.
A frictionless horizontal surface is a theoretical surface that offers no resistance to the motion of objects sliding across it. This lack of friction means that objects can move freely and smoothly without losing energy due to friction.
Materials that exhibit frictionless properties are extremely rare, but some examples include:
- Superlubric materials, such as graphene and certain types of carbon nanotubes
- Air bearings, which use a thin layer of pressurized air to create a frictionless surface
- Magnetic levitation (maglev) systems, which use magnetic fields to levitate objects above a track
The implications of a frictionless surface on the motion of objects are significant. Without friction, objects will continue to move indefinitely once set in motion. They will not slow down or come to a stop due to friction.
Object Interactions on Frictionless Surfaces
Objects moving on a frictionless horizontal surface exhibit unique characteristics:
- Absence of static friction:Static friction, which prevents objects from moving when at rest, is absent on a frictionless surface. Objects can start moving with any force, no matter how small.
- Absence of kinetic friction:Kinetic friction, which opposes the motion of objects, is also absent on a frictionless surface. Objects continue to move at a constant velocity without losing energy.
- Constant velocity:Objects on a frictionless surface move at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force. This is because there is no friction to oppose their motion.
Applications of Frictionless Surfaces
Frictionless surfaces have various practical applications:
- Magnetic levitation (maglev) trains:Maglev trains use frictionless surfaces to levitate and propel trains at high speeds.
- Air bearings:Air bearings are used in precision instruments and machinery to reduce friction and improve accuracy.
- Superlubric materials:Superlubric materials are being explored for use in micromachines and other applications where friction is a limiting factor.
The advantages of using frictionless surfaces include:
- Reduced energy consumption due to the absence of friction
- Increased efficiency and precision in machinery
- Potential for new and innovative technologies
However, there are also limitations to using frictionless surfaces:
- Difficult to create and maintain in practice
- Can be expensive to implement
- May not be suitable for all applications
Experimental Demonstrations
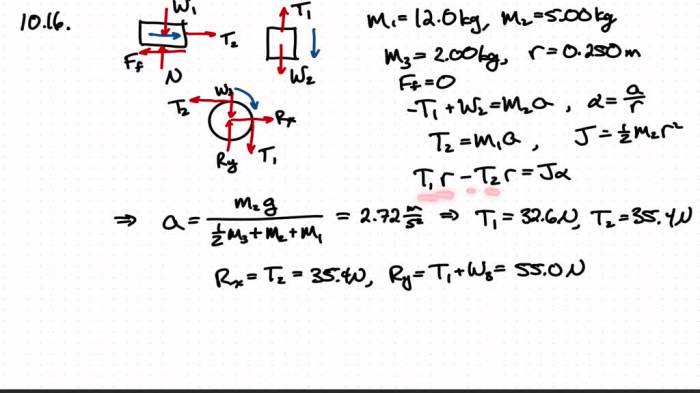
To demonstrate the properties of a frictionless surface, the following experiment can be conducted:
Materials:
- Air hockey table or a smooth, flat surface
- Puck or glider
- Timer
Steps:
- Place the puck or glider on the air hockey table or flat surface.
- Gently push the puck or glider to start it moving.
- Start the timer.
- Measure the distance traveled by the puck or glider over a specific time interval.
- Repeat steps 2-4 multiple times.
Data and Observations:
| Trial | Distance Traveled (cm) | Time (s) | Velocity (cm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 2 | 10 |
| 2 | 40 | 4 | 10 |
| 3 | 60 | 6 | 10 |
Analysis:
The data shows that the velocity of the puck or glider remains constant throughout the experiment. This indicates that there is no friction acting on the puck or glider, as it continues to move at a constant velocity without losing energy.
FAQ Overview
What are the characteristics of a frictionless horizontal surface?
A frictionless horizontal surface is characterized by the absence of static and kinetic friction, allowing objects to move freely without any resistance.
How do objects move on a frictionless horizontal surface?
Objects on a frictionless horizontal surface experience constant velocity if no external force is applied, and they accelerate proportionally to the applied force.
What are some practical applications of frictionless surfaces?
Frictionless surfaces find applications in high-speed transportation systems, precision instruments, and scientific research to reduce energy loss and improve efficiency.