The biology of skin color worksheet embarks on an enthralling journey into the intricate world of human diversity, where genetics, physiology, evolution, and sociocultural factors intertwine to paint a vibrant canvas of skin tones. Prepare to delve into a captivating narrative that illuminates the fascinating science behind our skin’s hues.
From the genetic blueprint that determines melanin production to the physiological adaptations that respond to environmental stimuli, this worksheet unravels the complex mechanisms that govern skin color. We’ll explore the evolutionary forces that have shaped human skin tones across diverse climates and environments, and delve into the profound social and cultural implications that skin color has carried throughout history.
Genetics of Skin Color: Biology Of Skin Color Worksheet
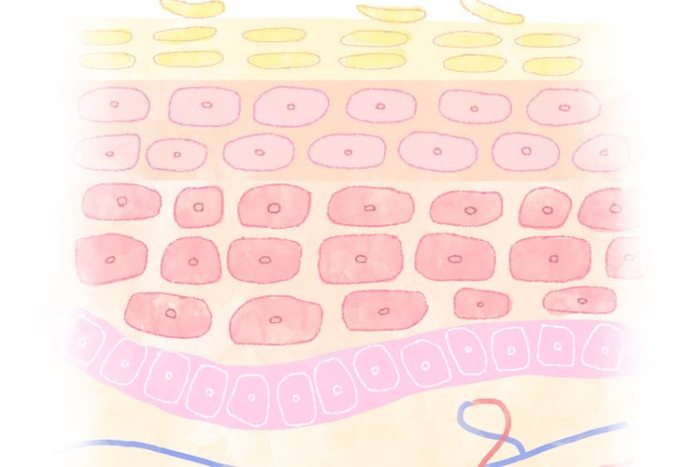
Skin color is a complex trait influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors. The primary determinant of skin color is melanin, a pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes. Melanin exists in two forms: eumelanin (brown-black) and pheomelanin (red-yellow). The relative amounts and distribution of these pigments determine an individual’s skin tone.
Genetic Variations Affecting Skin Color, Biology of skin color worksheet
Variations in several genes contribute to the wide range of skin colors observed in humans. One key gene is the melanocortin-1 receptor (MC1R), which regulates the production and distribution of melanin. Mutations in MC1R can lead to red hair and fair skin, as seen in individuals with the MC1R R allele.
Other genes involved in melanin synthesis, such as the tyrosinase gene (TYR), also exhibit variations that affect skin color.
Physiological Factors Influencing Skin Color
Skin color is influenced by a complex interplay of genetic and physiological factors. In addition to the genetics discussed earlier, physiological factors also play a significant role in determining the shade and variations of our skin. These factors include exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, hormonal influences, dietary habits, and skin disorders.
Role of UV Radiation in Skin Color Changes
Exposure to UV radiation, primarily from sunlight, is a major factor influencing skin color. When UV rays penetrate the skin, they interact with a pigment called melanin, produced by cells called melanocytes. Melanin acts as a natural sunscreen, absorbing and scattering UV radiation, protecting the skin from damage.The
amount of melanin produced varies from person to person, contributing to different skin colors. People with higher melanin levels have darker skin tones, while those with lower levels have lighter skin tones. UV radiation triggers an increase in melanin production, resulting in tanning.
This process is the body’s natural defense mechanism to protect the skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation.
Hormonal and Dietary Influences on Skin Color
Hormonal fluctuations can also affect skin color. During pregnancy, increased levels of the hormone estrogen can lead to a darkening of the skin, particularly in areas like the face, nipples, and underarms. This condition, known as melasma, usually fades after childbirth.Diet
can also influence skin color to some extent. A deficiency in certain vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin B12 and iron, can cause skin to appear pale or yellowish. Conversely, excessive consumption of certain foods, such as carrots, can lead to a yellowing of the skin known as carotenemia.
Impact of Skin Disorders and Medical Conditions on Skin Color
Various skin disorders and medical conditions can affect skin color. For instance, vitiligo is a condition that causes patches of skin to lose their pigment, resulting in white patches on the skin. On the other hand, certain medical conditions, such as Addison’s disease, can lead to a darkening of the skin due to increased production of melanin.Understanding
Diving into the complexities of skin color in biology class? For those seeking additional insights, don’t miss out on the comprehensive periop 101 final exam answers . This invaluable resource offers a thorough understanding of perioperative concepts, complementing your studies in skin color biology.
the physiological factors influencing skin color provides a comprehensive perspective on the complex mechanisms that determine our skin’s appearance. These factors interact with genetic influences to create the diverse range of skin colors we observe in human populations.
Evolutionary Adaptations of Skin Color

Skin color has evolved over time due to various selective pressures, primarily driven by the need for protection against ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun and adaptation to different environmental conditions.
In regions with high levels of UV radiation, such as near the equator, darker skin color provides protection against skin damage and skin cancer. Melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, absorbs UV radiation, reducing its penetration into the skin.
Conversely, in regions with lower UV radiation levels, lighter skin color allows for better absorption of sunlight, facilitating vitamin D synthesis.
Geographic Variations
As humans migrated to different parts of the world, their skin color adapted to the local climate and environment. For example:
- People living in equatorial regions, where UV radiation is intense, typically have darker skin tones.
- Populations in temperate regions, with moderate UV radiation levels, have intermediate skin tones.
- Inhabitants of high-latitude regions, where UV radiation is less intense, often have lighter skin tones.
Examples of Evolutionary Adaptations
Various species exhibit variations in skin color due to evolutionary adaptations. For instance:
- Polar bears have white fur to camouflage in their snowy habitat.
- Melanistic leopards have dark fur to blend in with their dark forest surroundings.
li>Desert-dwelling lizards have light-colored skin to reflect sunlight and stay cool.
Query Resolution
What is the primary determinant of skin color?
Melanin, a pigment produced by cells in the skin, plays the primary role in determining skin color.
How does UV radiation influence skin color?
Exposure to UV radiation triggers the production of melanin, leading to darkening of the skin as a protective response.
What are some examples of genetic variations that affect skin color?
Variations in genes involved in melanin production, such as the MC1R gene, can lead to differences in skin color.
How has skin color adapted to different climates and environments?
Over time, human populations have evolved adaptations in skin color to suit the prevailing environmental conditions, such as increased melanin production in regions with high UV radiation.
